What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 9 And 21
faraar
Sep 13, 2025 · 7 min read
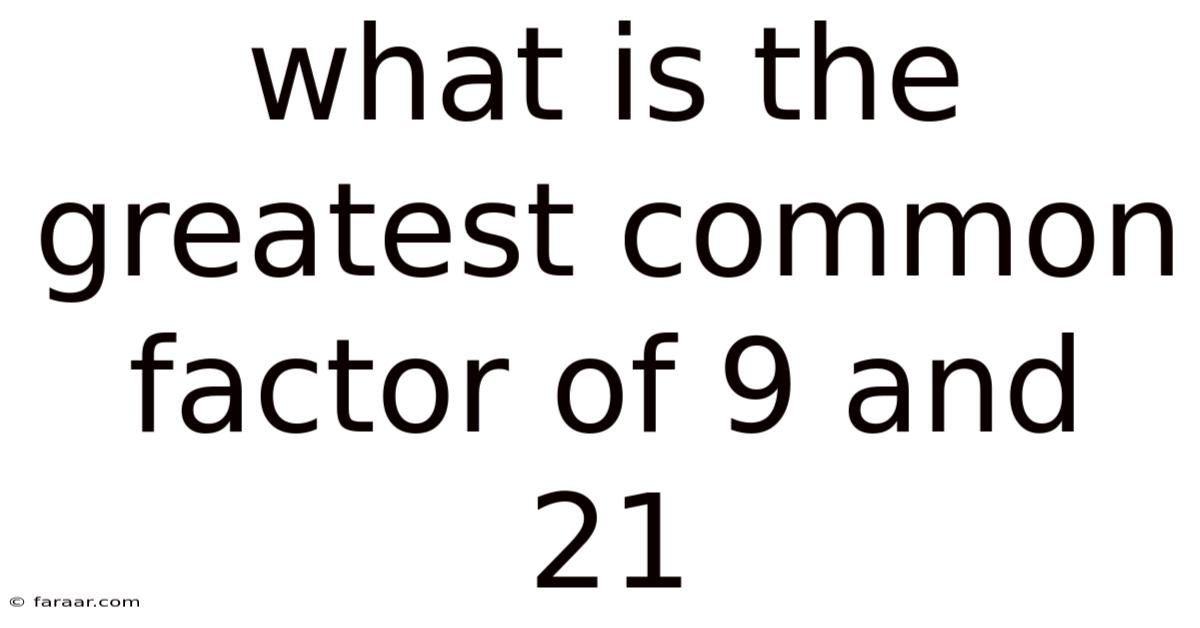
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Greatest Common Factor: A Deep Dive into 9 and 21
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task. But understanding the underlying concepts and different methods for calculating the GCF not only helps solve this specific problem for 9 and 21, but also builds a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. This article will explore various approaches to finding the GCF of 9 and 21, delve into the mathematical principles involved, and extend the discussion to broader applications. We'll uncover why understanding the GCF is crucial in various fields, from simplifying fractions to solving complex algebraic equations.
Understanding the Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
The greatest common factor (GCF) of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that perfectly divides both numbers. For example, the GCF of 12 and 18 is 6 because 6 is the largest number that divides both 12 and 18 evenly.
Understanding the GCF is foundational in many areas of mathematics. It simplifies fractions, helps in solving algebraic equations, and plays a crucial role in number theory. It’s a building block for more complex mathematical operations and concepts.
Finding the GCF of 9 and 21: Method 1 - Listing Factors
The most straightforward method to find the GCF is by listing all the factors of each number and then identifying the largest factor they share.
Factors of 9: 1, 3, 9
Factors of 21: 1, 3, 7, 21
By comparing the lists, we see that the common factors of 9 and 21 are 1 and 3. The largest of these common factors is 3. Therefore, the greatest common factor of 9 and 21 is 3.
This method is suitable for smaller numbers, but it can become cumbersome and inefficient when dealing with larger numbers with many factors.
Finding the GCF of 9 and 21: Method 2 - Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a more efficient method, especially for larger numbers. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors – numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
- Prime factorization of 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
- Prime factorization of 21: 3 x 7
Once we have the prime factorizations, we identify the common prime factors and their lowest powers. In this case, the only common prime factor is 3, and its lowest power is 3¹ (or simply 3). Therefore, the greatest common factor of 9 and 21 is 3.
This method is more systematic and less prone to error than the listing factors method, particularly when dealing with larger numbers.
Finding the GCF of 9 and 21: Method 3 - Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCF of two numbers, especially when dealing with larger numbers. It's based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers doesn't change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal, and that number is the GCF.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to 9 and 21:
- Start with the larger number (21) and the smaller number (9).
- Divide the larger number (21) by the smaller number (9): 21 ÷ 9 = 2 with a remainder of 3.
- Replace the larger number with the remainder (3). Now we have the numbers 9 and 3.
- Repeat the process: Divide 9 by 3: 9 ÷ 3 = 3 with a remainder of 0.
- Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the last non-zero remainder, which is 3.
The Euclidean algorithm is a powerful tool because it efficiently reduces the problem to smaller, more manageable numbers, making it ideal for larger integers where listing factors or prime factorization becomes less practical.
Mathematical Principles Behind the GCF
The concept of the GCF is deeply rooted in number theory and has significant implications in various mathematical fields. Understanding the underlying principles enhances our grasp of its applications.
- Divisibility Rules: Understanding divisibility rules for various numbers (e.g., divisibility by 2, 3, 5, etc.) can help quickly identify potential common factors.
- Prime Numbers: Prime numbers are the building blocks of all integers. Prime factorization is essential for efficiently finding the GCF of larger numbers. The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers.
- Modular Arithmetic: The concept of remainders, central to the Euclidean algorithm, is a key element of modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with widespread applications in cryptography and computer science.
Applications of the GCF
The GCF isn't just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in various fields:
- Simplifying Fractions: The GCF is used to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 21/9 can be simplified to 7/3 by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF, which is 3.
- Solving Algebraic Equations: The GCF plays a role in factoring algebraic expressions, which is crucial in solving equations and simplifying complex mathematical expressions.
- Geometry and Measurement: The GCF is used in solving problems related to area, volume, and measurement conversions. For instance, finding the largest square tile that can perfectly cover a rectangular floor involves finding the GCF of the floor's dimensions.
- Number Theory: The GCF is a fundamental concept in number theory, which explores the properties of integers. It's used in advanced mathematical concepts such as modular arithmetic and cryptography.
- Computer Science: Efficient algorithms for calculating the GCF, like the Euclidean algorithm, are crucial in computer science for tasks involving large numbers and cryptographic operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Is the GCF always smaller than the numbers involved?
A: Yes, the GCF is always less than or equal to the smallest of the numbers involved. It can be equal only if one number is a multiple of the other.
-
Q: What is the GCF of two prime numbers?
A: The GCF of two distinct prime numbers is always 1 because prime numbers only have 1 and themselves as factors.
-
Q: Can the GCF be zero?
A: No, the GCF is always a positive integer. It cannot be zero because zero is not a factor of any positive integer.
-
Q: What if I have more than two numbers? How do I find their GCF?
A: You can extend the methods discussed above (prime factorization or Euclidean algorithm) to find the GCF of more than two numbers. For prime factorization, you find the common prime factors and their lowest powers across all numbers. For the Euclidean algorithm, you can iteratively find the GCF of pairs of numbers.
-
Q: Are there any online calculators or tools to find the GCF?
A: Yes, many online calculators and software programs are available to calculate the GCF of any set of numbers. These tools can be helpful for verifying your calculations or handling larger numbers. However, understanding the underlying principles is crucial for building a stronger mathematical foundation.
Conclusion
Finding the greatest common factor of 9 and 21, as demonstrated through various methods, is not just about arriving at the answer (3). It's about grasping the fundamental concepts of number theory, divisibility, and efficient algorithms. Understanding the GCF goes beyond simple arithmetic; it provides a solid base for more advanced mathematical concepts and has significant practical applications across multiple disciplines. By mastering the methods presented here—listing factors, prime factorization, and the Euclidean algorithm—you'll be equipped to tackle more complex GCF problems and appreciate the significance of this fundamental mathematical concept. Remember, the journey of understanding mathematical concepts is as important as the destination of finding the correct answer. So, keep exploring, keep questioning, and keep learning!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Square Root Of 13 A Rational Number
Sep 13, 2025
-
Find The Value Of The Linear Correlation Coefficient R
Sep 13, 2025
-
P 2w 2l Solve For L
Sep 13, 2025
-
How To Start A Speech For Graduation
Sep 13, 2025
-
8 Is What Percent Of 12 5
Sep 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 9 And 21 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.