Is Negative 5 A Whole Number
faraar
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
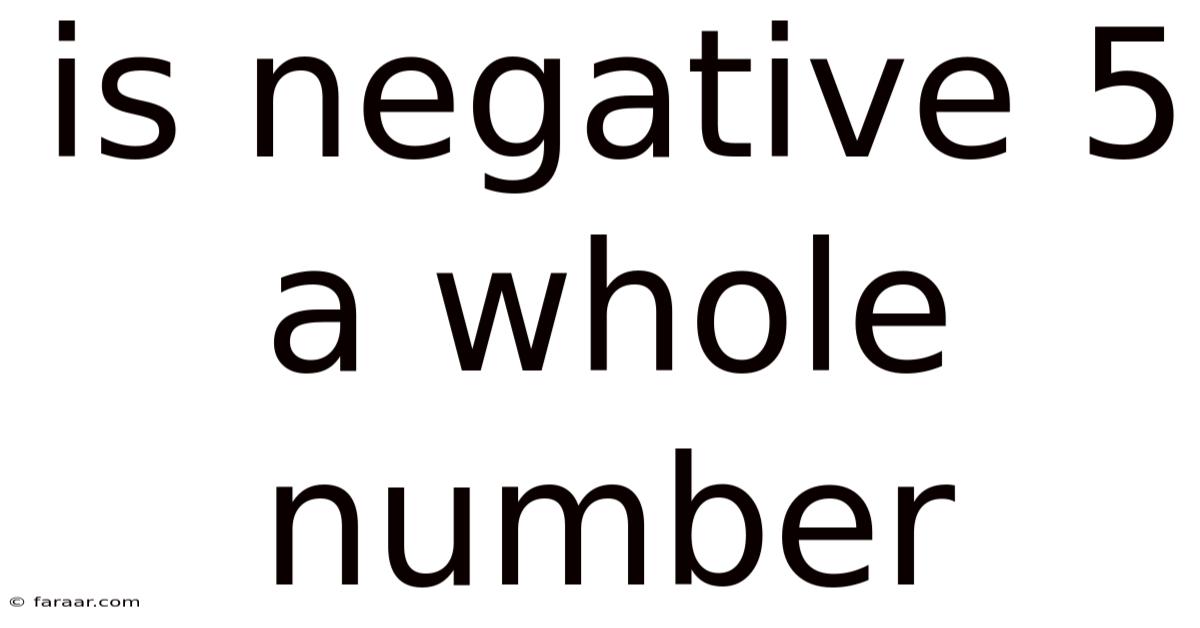
Table of Contents
Is Negative 5 a Whole Number? A Deep Dive into Number Systems
The question, "Is negative 5 a whole number?" might seem simple at first glance. However, understanding the answer requires a deeper exploration into the fascinating world of number systems. This article will not only answer the question definitively but also provide a comprehensive overview of different number sets, their properties, and their relationships, clarifying the precise definition of whole numbers and their place within the broader mathematical landscape. This will equip you with a robust understanding of numerical classifications and solidify your foundational knowledge of mathematics.
Introduction to Number Systems
Mathematics is built upon a foundation of numbers. Over centuries, mathematicians have developed various classifications to categorize these numbers based on their properties. Understanding these classifications is key to answering our core question and grasping the broader context of numerical relationships. The key number sets we'll explore include:
- Natural Numbers (N): These are the counting numbers, starting from 1 and extending infinitely: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ...}
- Whole Numbers (W): This set includes all natural numbers and zero: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ...}
- Integers (Z): This set encompasses all whole numbers and their negative counterparts: {... -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...}
- Rational Numbers (Q): These are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers, and q is not zero. This includes all integers, as well as fractions and terminating or repeating decimals.
- Irrational Numbers: These numbers cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. They have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal representations. Examples include π (pi) and √2.
- Real Numbers (R): This set encompasses all rational and irrational numbers. It represents all numbers on the number line.
- Complex Numbers (C): These numbers extend beyond real numbers and include imaginary numbers (numbers involving the square root of -1, denoted as i).
Defining Whole Numbers
The core of our question hinges on the precise definition of whole numbers. Whole numbers are non-negative integers. This means they include zero and all positive integers, but crucially, they exclude negative numbers. The set of whole numbers begins with zero and continues indefinitely in the positive direction. This seemingly simple distinction is vital for accurately classifying numbers.
Is -5 a Whole Number? The Definitive Answer
Given the definition of whole numbers, the answer is unequivocally no. Negative 5 (-5) is an integer, and it is a negative integer. However, because whole numbers, by definition, are non-negative, -5 falls outside the set of whole numbers.
Why the Distinction Matters
Understanding the difference between integers and whole numbers is crucial for several reasons:
- Mathematical Operations: Certain mathematical operations behave differently depending on the type of number involved. For example, the square root of a negative whole number is not a real number, leading to the concept of imaginary numbers.
- Problem Solving: Accurately identifying the type of numbers involved in a problem is critical for selecting appropriate solution methods. A problem involving whole numbers might require different strategies compared to a problem involving integers or rational numbers.
- Computer Science: Computer programming often relies on distinct data types to represent different number sets. Understanding the limitations and characteristics of whole numbers is essential for writing efficient and accurate code.
- Real-World Applications: Many real-world applications deal with quantities that are inherently non-negative, such as counting objects, measuring lengths (positive values), or representing quantities like population or age. Whole numbers are perfectly suited to model these scenarios.
Visualizing Number Sets
It can be helpful to visualize the relationships between these number sets using Venn diagrams. Imagine a series of nested circles. The innermost circle would represent natural numbers. The next circle would encompass whole numbers (including zero). The next would include integers (incorporating negative numbers), followed by rational numbers, irrational numbers (which don't overlap with the others), and finally, the encompassing circle of real numbers. Complex numbers would extend beyond this visual representation.
Further Exploration of Number Properties
Beyond their classification into sets, numbers possess various other properties:
- Even and Odd Numbers: Integers are classified as even or odd based on their divisibility by 2.
- Prime and Composite Numbers: Natural numbers greater than 1 are either prime (only divisible by 1 and themselves) or composite (divisible by other numbers besides 1 and themselves).
- Factors and Multiples: Factors are numbers that divide evenly into a given number, while multiples are the results of multiplying a number by integers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between an integer and a whole number?
A: Whole numbers are non-negative integers (0, 1, 2, 3...). Integers include whole numbers and their negative counterparts (... -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3...). The key difference is that whole numbers exclude negative numbers.
Q: Can a whole number be negative?
A: No. By definition, whole numbers are non-negative.
Q: Are all whole numbers integers?
A: Yes. All whole numbers are integers, but not all integers are whole numbers.
Q: What is the smallest whole number?
A: The smallest whole number is 0.
Q: Are decimals whole numbers?
A: No. Whole numbers are integers; decimals represent fractional parts.
Q: Why is zero considered a whole number?
A: Zero represents the absence of quantity and serves as a crucial point of reference in many mathematical operations and number systems. Its inclusion in the whole number set provides a complete and consistent system for representing quantities.
Conclusion: Understanding Numerical Classifications
The question of whether -5 is a whole number highlights the importance of precise definitions in mathematics. While -5 is an integer, it does not belong to the set of whole numbers because whole numbers, by definition, are non-negative. Understanding the nuances between different number sets—natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, real numbers, and complex numbers—is foundational to advanced mathematical concepts and applications across various fields. This exploration has not only provided a definitive answer to our initial question but also equipped you with a deeper understanding of number systems and their properties, empowering you to confidently navigate the mathematical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Point O Is The Center Of The Circle
Sep 23, 2025
-
How Many 1 4 Are In 2 Cups
Sep 23, 2025
-
The Probability That A Randomly Selected
Sep 23, 2025
-
Whats 1 3 Plus 1 3 In Cooking
Sep 23, 2025
-
How To Make An Excel Sheet Read Only
Sep 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Negative 5 A Whole Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.